Accurate acid volume measurement relies on volumetric analysis‚ specifically titration‚ demanding precise methods․ Resources like PDF documents detail equipment; burettes‚ pipettes‚ and flasks are crucial․
Understanding these methods‚ alongside accessing online resources‚ is vital for reliable results in quantitative chemical analysis‚ determining reactant concentrations effectively․
Importance of Accurate Volume Measurement in Acid Analysis
Precise volume measurement is paramount in acid analysis‚ directly impacting the reliability of quantitative results․ Titration‚ a core technique‚ hinges on accurately determining the volume of titrant reacting with the analyte․ Errors in volume measurement propagate through calculations‚ leading to inaccurate concentration determinations․
The selection of appropriate equipment‚ detailed in resources like PDF guides‚ is critical․ Burettes ensure precise titrant delivery‚ while pipettes guarantee accurate analyte volume measurement․ Volumetric flasks are essential for preparing standard solutions of known concentration․ Utilizing calibrated glassware and understanding potential sources of error – systematic and random – are vital․
Furthermore‚ standardization of acid solutions‚ often employing primary standards like Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP)‚ necessitates meticulous volume measurements․ Accessing relevant PDF documents outlining proper techniques and error analysis protocols is crucial for maintaining analytical rigor and ensuring the validity of experimental data․ Accurate measurements underpin the entire analytical process․
Overview of Common Acid Volume Measurement Techniques
Several techniques are employed for accurate acid volume measurement‚ with titration being the most prevalent․ This method relies on the precise delivery and measurement of liquid volumes using specialized glassware․ Detailed guides‚ often available as PDF documents‚ illustrate these techniques․
Key equipment includes burettes for titrant delivery‚ pipettes for analyte measurement‚ and volumetric flasks for standard solution preparation․ Automated titrators offer enhanced precision and efficiency‚ minimizing human error․ Gravimetric analysis‚ while measuring mass‚ complements volumetric methods in certain applications․
Understanding the principles of each technique‚ as outlined in analytical chemistry resources and PDF manuals‚ is crucial․ Proper calibration and handling of glassware are essential to minimize systematic errors․ Online resources and laboratory protocols provide detailed instructions on performing these measurements accurately‚ ensuring reliable analytical results․ Careful technique selection is vital for optimal outcomes․

Titration: The Core Method
Titration‚ a central technique‚ utilizes precise volume measurements․ PDF guides detail equipment like burettes and pipettes for accurate titrant and analyte delivery during analysis․
Principle of Titration for Acid-Base Analysis
Titration’s core principle involves the quantitative reaction between an acid and a base‚ meticulously determining the unknown concentration of one solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration․ This process hinges on accurately measuring the volume of the titrant required to reach the reaction’s endpoint․
Essential equipment‚ often detailed in laboratory PDF manuals‚ includes burettes for precise titrant delivery‚ pipettes for accurate analyte volume measurement‚ and appropriate glassware for solution preparation․ The reaction proceeds until neutralization is achieved‚ indicated by a color change or other detectable signal․
Understanding the stoichiometry of the reaction is paramount; the balanced chemical equation dictates the molar ratio between the acid and base․ Accurate volume readings‚ coupled with known concentrations‚ allow for precise calculation of the unknown concentration․ Resources emphasize careful technique to minimize errors and ensure reliable results․ The ‘titre’‚ or volume of titrant reacted‚ is a critical value in this calculation․
Furthermore‚ proper standardization of solutions‚ using primary standards like KHP‚ is crucial for establishing accurate concentrations‚ as detailed in analytical chemistry PDF guides․
Titrant and Analyte: Defining the Components
In acid-base titration‚ the analyte is the solution with an unknown concentration that we aim to determine․ Conversely‚ the titrant is the solution of precisely known concentration used to react with the analyte․ Accurate measurement of both solutions’ volume is paramount for precise analysis․
Selecting appropriate equipment‚ often outlined in laboratory PDF resources‚ is crucial․ Burettes are used for the controlled delivery of the titrant‚ while pipettes ensure accurate volume transfer of the analyte․ Volumetric flasks are essential for preparing standard solutions of known concentration․
The choice of titrant and analyte depends on the specific acid-base reaction being studied․ Understanding their respective properties‚ including molarity and stoichiometry‚ is vital․ Detailed PDF guides often illustrate proper handling and safety precautions for various acids and bases․

Precise volume readings from calibrated glassware‚ combined with knowledge of the reaction’s stoichiometry‚ allow for accurate calculation of the analyte’s concentration․ Maintaining meticulous technique minimizes errors and ensures reliable results‚ as emphasized in analytical chemistry manuals․
Endpoint and Equivalence Point in Titration
During titration‚ the endpoint signifies the observable change indicating reaction completion – often a color change from an indicator․ The equivalence point‚ however‚ represents the stoichiometric completion of the reaction‚ where moles of acid equal moles of base․ Ideally‚ these points coincide‚ but discrepancies can occur․
Selecting the correct indicator‚ detailed in analytical chemistry PDF guides‚ is crucial for a clear endpoint․ Equipment like burettes with precise graduations allow for accurate volume determination at the endpoint․ Automated titrators‚ described in advanced resources‚ minimize subjective endpoint detection․
Understanding the difference between endpoint and equivalence point is vital for error analysis․ Factors like indicator choice and reaction kinetics can influence their divergence․ PDF documents often provide titration curves illustrating this relationship;
Accurate volume measurement using calibrated glassware‚ coupled with careful observation of the endpoint‚ allows for a close approximation of the equivalence point․ Proper technique and understanding of potential errors are essential for reliable quantitative analysis․

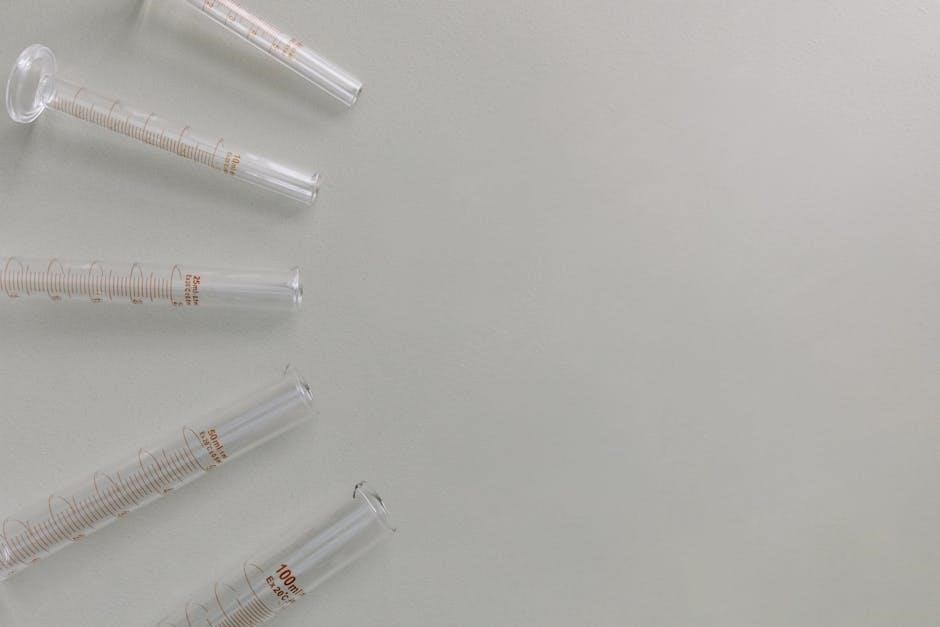
Volumetric Glassware: Essential Tools
Precise volume measurement demands calibrated glassware: burettes‚ pipettes‚ and flasks․ PDF resources detail proper usage and calibration of this equipment for accurate acid analysis․
Burettes: Precise Delivery of Titrant
Burettes are graduated glass tubes‚ essential for the precise delivery of titrant during volumetric analysis‚ particularly in acid-base titrations․ Their design allows for accurate volume control‚ crucial for determining the endpoint of a titration․ PDF guides often illustrate proper burette handling‚ including filling‚ reading the meniscus‚ and performing accurate titrations․
Selecting the appropriate burette size depends on the expected titrant volume․ Common types include glass and Teflon burettes‚ each offering varying chemical resistance․ Careful calibration is paramount; systematic errors can arise from inaccurate graduations․ Resources detail calibration procedures‚ ensuring reliable results․
Proper technique involves slow‚ controlled addition of titrant‚ observing the reaction carefully․ Stopcocks control the flow rate‚ demanding precise manipulation․ Online resources and PDF documents emphasize the importance of rinsing the burette with the titrant before use‚ avoiding contamination and ensuring accurate volume delivery․ Mastering burette technique is fundamental to accurate acid analysis․
Pipettes: Accurate Measurement of Analyte Volume
Pipettes are indispensable tools for accurately measuring the volume of the analyte in acid-base titrations․ Unlike burettes which deliver variable volumes‚ pipettes deliver a fixed‚ pre-determined volume with high precision․ Numerous PDF resources detail different pipette types – volumetric‚ graduated‚ and Pasteur – each suited for specific applications․
Volumetric pipettes‚ designed for a single volume‚ offer the highest accuracy․ Graduated pipettes allow for dispensing variable volumes within their capacity․ Proper technique is vital: vertical positioning‚ complete drainage‚ and avoiding parallax errors are crucial․ Online guides emphasize these points․
Calibration of pipettes‚ as outlined in analytical chemistry PDFs‚ is essential to ensure accuracy․ Factors like temperature can affect volume‚ requiring corrections․ Careful rinsing with the analyte before use prevents contamination․ Mastering pipette technique‚ alongside understanding calibration procedures‚ guarantees reliable analyte volume measurement․
Volumetric Flasks: Preparing Standard Solutions
Volumetric flasks are fundamental for preparing standard solutions with known concentrations‚ crucial for accurate acid analysis․ These flasks‚ detailed in numerous analytical chemistry PDF guides‚ are designed to contain a precise volume at a specific temperature‚ typically 20°C․ Their narrow necks minimize error during dilution․
The process involves dissolving a precisely weighed amount of solute (acid) in a solvent‚ then carefully adding solvent to the flask until the meniscus reaches the etched calibration mark․ Many online resources and PDF documents emphasize the importance of viewing the meniscus at eye level to avoid parallax errors․
Proper mixing is vital to ensure homogeneity․ Inverting the flask multiple times‚ rather than shaking‚ achieves thorough dissolution․ Calibration of volumetric flasks‚ as described in laboratory manuals and PDFs‚ verifies their accuracy․ Accurate standard solutions are the cornerstone of reliable titrimetric analysis‚ demanding meticulous flask usage․
Types of Titration for Acid Analysis
Titration types—strong/strong‚ weak/strong‚ strong/weak—require precise volume control․ PDF resources detail equipment like burettes and volume measurement techniques for accurate analysis․
Strong Acid-Strong Base Titrations
Strong acid-strong base titrations represent a foundational technique in quantitative analysis‚ demanding meticulous volume measurement․ Essential equipment‚ detailed in numerous PDF guides and online resources‚ includes burettes for precise titrant delivery‚ ensuring accurate volume control throughout the process․
Pipettes are critical for accurately measuring the analyte volume‚ while volumetric flasks facilitate the preparation of standard solutions with known concentrations․ The selection of appropriate glassware‚ often outlined in laboratory manuals available as PDF downloads‚ is paramount for minimizing errors․
Automated titrators‚ discussed in advanced resources‚ further enhance precision and efficiency․ Understanding the principles of titration‚ coupled with proper equipment utilization—as illustrated in instructional PDFs—allows for reliable determination of unknown acid or base concentrations․ Careful attention to glassware calibration and technique is vital for achieving accurate results in these fundamental titrations․
Weak Acid-Strong Base Titrations
Weak acid-strong base titrations necessitate precise volume measurements‚ relying on specialized equipment detailed in analytical chemistry PDF resources․ Burettes remain central for controlled titrant addition‚ demanding careful reading and calibration to minimize errors․ Pipettes are crucial for accurate analyte volume transfer‚ ensuring stoichiometric calculations are reliable․
Volumetric flasks are essential for preparing standardized strong base solutions‚ with concentration accuracy verified through primary standards—information readily available in laboratory technique PDFs․ Understanding buffer regions and pH changes during titration‚ often illustrated in online resources‚ is vital for endpoint determination․
Advanced techniques‚ like utilizing automated titrators (described in specialized PDF documentation)‚ enhance precision and reduce subjective error․ Proper equipment selection‚ coupled with adherence to established protocols outlined in analytical chemistry guides‚ guarantees accurate results when quantifying weak acid concentrations․ Careful consideration of the weak acid’s dissociation constant is also key․
Strong Acid-Weak Base Titrations
Strong acid-weak base titrations demand meticulous volume control‚ with equipment specifications often detailed in analytical chemistry PDF guides․ Burettes are paramount for precise titrant delivery‚ requiring regular calibration and careful meniscus reading to minimize systematic errors․ Pipettes ensure accurate analyte volume measurement‚ crucial for stoichiometric calculations and reliable results․
Volumetric flasks are essential for preparing standardized strong acid solutions‚ with concentration verification relying on primary standards—information found in laboratory technique PDFs․ Understanding the formation of the weak base’s conjugate acid and the resulting pH changes is vital‚ often visualized in online resources․
Automated titrators‚ discussed in specialized PDF documentation‚ can enhance precision and reduce subjective endpoint determination․ Proper equipment maintenance‚ alongside adherence to established protocols outlined in analytical manuals‚ guarantees accurate quantification of weak base concentrations․ Accessing relevant PDFs detailing buffer capacity is also beneficial․

Standardization of Acid Solutions
Accurate concentration determination utilizes primary standards‚ detailed in analytical PDFs․ Burettes and pipettes are vital for precise volume measurements during standardization processes‚ ensuring reliable results․
Using Primary Standards for Accurate Concentration Determination
Primary standards are exceptionally pure‚ stable compounds crucial for accurately establishing the concentration of acid solutions․ Their use minimizes errors inherent in direct preparation․ Detailed procedures‚ often found in analytical chemistry PDF resources‚ outline the precise methodologies for employing these standards․
Volumetric glassware plays a pivotal role․ Burettes deliver precise volumes of titrant during standardization‚ while pipettes accurately measure the primary standard solution․ Volumetric flasks are essential for preparing solutions of known concentration․ The accuracy of these instruments directly impacts the reliability of the determined acid concentration․
Careful measurement of volumes‚ coupled with meticulous weighing of the primary standard‚ is paramount․ Online resources and laboratory manuals often provide guidance on proper technique․ The process involves reacting a known mass of the primary standard with the acid solution‚ then performing a titration to determine the endpoint․ This allows for a precise calculation of the acid’s molarity‚ ensuring accurate results in subsequent analyses․ Accessing relevant PDF documents detailing these procedures is highly recommended․
Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate (KHP) as a Common Standard
Potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHP) is a widely utilized primary standard for acid-base titrations due to its stability‚ high purity‚ and non-hygroscopic nature․ Detailed protocols‚ often available in analytical chemistry PDF guides‚ demonstrate its effective use in standardizing base solutions‚ which are then used to determine acid concentrations․
Accurate measurement of KHP requires precise volumetric glassware․ Analytical balances are essential for weighing the KHP to a high degree of accuracy; Burettes are used to deliver the titrant‚ while pipettes accurately transfer the KHP solution․ These instruments‚ discussed in various laboratory resource PDFs‚ are critical for minimizing errors․
The reaction between KHP and the acid is well-defined‚ allowing for precise stoichiometric calculations․ Online resources and laboratory manuals provide detailed instructions on performing the titration and calculating the acid’s concentration․ Proper technique‚ including careful observation of the endpoint‚ is crucial․ Accessing comprehensive PDF documentation on KHP standardization ensures reliable and reproducible results;

Error Analysis in Acid Volume Measurement
Systematic and random errors impact accuracy․ PDF guides detail calibration of volumetric glassware – burettes‚ pipettes‚ and flasks – to minimize these‚ ensuring reliable acid concentration data․
Systematic Errors and Their Mitigation
Systematic errors in acid volume measurement consistently skew results in one direction․ These often stem from improperly calibrated volumetric glassware – burettes‚ pipettes‚ and flasks – or inherent flaws in the equipment itself․ PDF resources dedicated to analytical chemistry emphasize the importance of regular calibration against certified standards․
Temperature fluctuations can also introduce systematic errors‚ affecting the volume of both the acid and the titrant․ Maintaining a consistent laboratory temperature‚ or applying appropriate correction factors‚ is crucial․ Parallax errors‚ arising from incorrect eye-level reading of meniscus‚ are another common source․ Proper training and utilizing calibrated glassware with clear markings mitigate this․
Furthermore‚ contamination of equipment can lead to inaccurate volumes․ Thorough cleaning procedures‚ utilizing appropriate detergents and rinsing techniques‚ are essential․ Regularly inspecting glassware for chips or cracks‚ and replacing damaged equipment‚ prevents consistent under- or over-delivery of volumes․ Detailed protocols outlined in analytical chemistry PDF guides provide comprehensive mitigation strategies․
Random Errors and Statistical Analysis
Random errors‚ unlike systematic errors‚ fluctuate unpredictably in acid volume measurements․ These arise from factors like inconsistent reading of the meniscus‚ slight variations in dispensing technique‚ or minor temperature fluctuations․ While unavoidable‚ their impact can be minimized through repeated measurements and statistical analysis․
Performing multiple titrations – typically at least three – allows for the calculation of the mean‚ standard deviation‚ and confidence intervals․ PDF guides on analytical chemistry detail these statistical methods․ The standard deviation quantifies the spread of data‚ indicating the precision of the measurements․
Outliers‚ data points significantly deviating from the mean‚ should be identified and investigated․ While not always discarded‚ their inclusion can disproportionately affect statistical parameters․ Utilizing properly calibrated equipment – burettes‚ pipettes‚ and flasks – as detailed in equipment-specific PDF manuals‚ reduces random error․ Statistical software packages streamline these calculations‚ providing robust data analysis and ensuring reliable results despite inherent variability․
Advanced Techniques & Resources

Automated titrators enhance precision‚ while PDF resources detail equipment operation and maintenance․ Online databases offer access to analytical chemistry guides and equipment specifications․
Automated Titrators: Enhancing Precision and Efficiency
Automated titrators represent a significant advancement in acid-base analysis‚ moving beyond manual techniques to deliver superior precision and efficiency․ These instruments meticulously control titrant delivery‚ often utilizing a burette system coupled with sophisticated endpoint detection mechanisms․ PDF manuals accompanying these devices detail calibration procedures‚ ensuring accurate volume measurements․
Unlike manual titration‚ automated systems minimize subjective endpoint determination‚ relying on sensors – such as pH electrodes – to signal the equivalence point․ This reduces the impact of human error‚ leading to more reproducible results․ Many models feature data logging capabilities‚ automatically recording titration curves for detailed analysis and reporting․ Accessing equipment-specific PDF documentation is crucial for understanding these features․
Furthermore‚ automated titrators can significantly increase throughput‚ particularly in high-volume laboratories․ They can perform titrations unattended‚ freeing up analysts for other tasks․ Online resources and manufacturer websites often provide application notes and troubleshooting guides‚ supplementing the information found in PDF format․ The integration of robotic sample handling further streamlines the process‚ enhancing overall laboratory productivity․
Accessing Relevant PDF Documents and Online Resources
Comprehensive understanding of acid volume measurement necessitates access to detailed PDF documentation and a wealth of online resources․ Manufacturers of volumetric glassware – burettes‚ pipettes‚ and flasks – routinely provide PDF manuals outlining proper usage‚ calibration‚ and maintenance procedures․ These documents are vital for ensuring accuracy and traceability․
Beyond manufacturer resources‚ academic institutions and scientific organizations often publish PDF guides on titration techniques and error analysis․ Websites like those referenced previously (newi․ac․uk/buckleyc/titrat․htm) offer supplementary materials‚ including detailed explanations of redox titrations and related concepts․ Searching for “volumetric analysis PDF” yields numerous relevant results․

Furthermore‚ online databases and scientific literature repositories provide access to research articles detailing advanced titration methods and equipment․ Utilizing keywords like “acid-base titration PDF” or specific equipment model numbers refines search results․ Always prioritize resources from reputable sources to ensure the reliability of the information obtained‚ supplementing practical experience with theoretical knowledge․